![]() R. Craig Collins >Common
> How To: Terms
R. Craig Collins >Common
> How To: Terms
How To: Terms/Big Picture ©
R. Craig Collins, 2004/2018
TERMS BELOW
The following is a list of terms. The meanings are below, and will help as you begin reading the class textbooks...
Glossary
BIOS
Bit
Boot
Byte
CPU
Disk
Giga...
Hardware
Hertz
Input
Kilo...
Mega...
Monitor
Output
Peripheral
RAM
ROM
Software
Zip
Terms: Flash cards
Below are my definitions, which are explained a
little differently than your books do. Hopefully the combination of my definitions,
and the book definitions will help you master the terms. The Big Picture is below.
Access |
Locating a file |
Bandwidth |
Transmission capacity, often incorrectly referred to as transmission speed |
BIOS |
Basic Input/Output System, a ROM chip used at boot up, as the OS loads |
Bit |
Binary Digit, a 1 or a 0, the only item a computer can understand |
Byte |
Binary Term, usually 8 bits, enough information to represent a typed character |
CPU |
Central Processing Unit, the brains of the computer |
Computer Proficiency |
In order to use a computer, you don't have to be an expert, just proficient... |
CRT |
Cathode Ray Tube, a old fashioned boxy TV style monitor |
Data |
Facts that can be processed into useful information, input... YOUR stuff |
Desktop |
The metaphor used in a Windows computer to show what files and programs you may use, and how they are organized |
DOS |
Disk Operating System, a command line OS that came before Windows |
File |
In databases, a collection of related records; in computers in general, the name given to a collection of stored data / instructions |
Hard Disk |
Long memory that keeps content even when the computer is turned off… |
Hardware |
The part of the computer you can touch, if outside the case it is a 'peripheral' |
Hertz |
Repetitions, or cycles; often related as cycles per second, as in megahertz , about a million cycles |
| Icon | A graphical element on a desktop that represents an object, such as a file or program |
|
|
I/O |
Input/Output, typically a used as a hardware term. |
| Information | Data that has been processed info something useful; output (the computer communicating with the user, such as results displayed on a monitor) |
Instructions |
Software that performs a task (applications or programs): basically stored instructions. |
Kilo... |
about 1000, exactly 1024; can be used with bits, bytes, or hertz |
Mega... |
about a million, exactly 10242; can be used with bits, bytes, or hertz |
Microprocessor |
another name for CPU, see CPU |
O/S |
Operating System; a subset of System software; the OS provides the interface between the hardware, application software, and the user; i.e. DOS or Windows |
Program |
A file that contains instructions, such as a word processor, Application |
RAM |
Random Access Memory, (should’ve been Read Write Memory) |
ROM |
Read Only Memory, memory that holds unchanging information |
Software |
Instructions or data in RAM; the part of the computer you can't touch; includes System software (manages the computer, such as the Operating System, or Utilities, or Programming) and |
User Interface |
How the user interacts with the system software; Windows is a Graphical UI |
www |
World wide web; the area of the Internet that uses http protocol to transfer files written in html; |
Zip |
ZIP: A file that can contain multiple files, or more importantly, a file that is compressed to take up less space; useful for emailing attachments, or for uploading. (See page 10) |
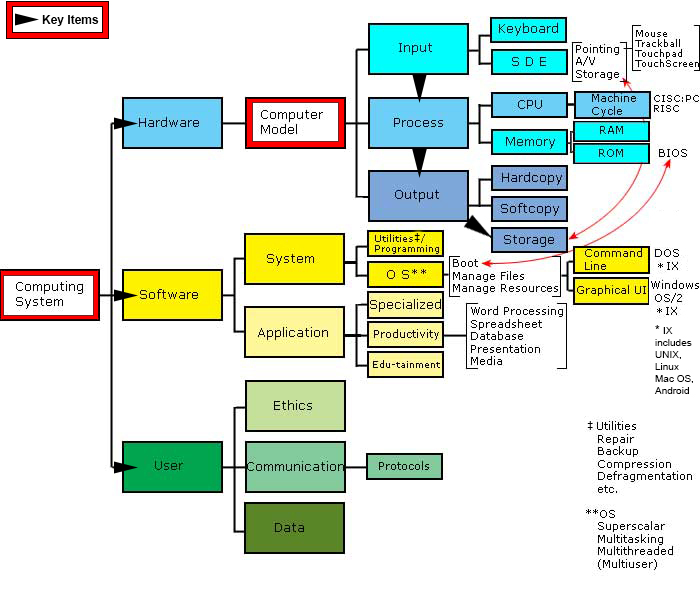
The COMPUTING SYSTEM
¯
|
|-----------------†----------------|
Hardware Software User
| | |
(The COMPUTING MODEL) | †®Data
¯ |
| |
|---------†----------| |
Input Process Output |
(Data) >>>> (Information)|
Keyboard CPU Monitor |
|
|
|-------†-------|
System Application
| |
|---------------†-----| †®Word Processing
Operating System Utilities †®Spreadsheet
| | †®Presentation Graphics
Windows XP |
|
†®Disk Repair
†®Backup
†®etc.
Note: Many people consider the Computer model to include 4 functions:
input®process ®output
and store
